|

1. DIFFERENCES IN REACTION RATES
OF THE OXIDATION
OF DIFFERENT ALCOHOLS
The objective of the experiment is
to examine the kinetics of the oxidation of methanol, ethanol, propan-1-ol and
propan-2-ol with potassium dichromate in acidic solution using the SpektraTM
spectrometer.
Hazards
|

|
Potassium
dichromate is very toxic and dangerous to the environment. It is harmful in
contact with skin and may cause sensitization by skin contact. It is toxic if
swallowed. Wear protective gloves and goggles and avoid release to the
environment.
R: 49-46-21-25-26-37/38-41-43-50/53 S: 53-45-60-61
|
 |
|
|
Sulphuric
acid is corrosive and causes severe burns. Wear suitable protective clothing,
gloves and eye protection.
R: 35 S: 26-30-36/37/39-45
|
|

|
Methanol
is flammable and toxic. Inhalation may cause cough, dizziness, headache, nausea, weakness and visual disturbance. It
may be absorbed through skin and may cause redness and dry skin. Wear
protective gloves.
R: 11-23/24/25-39/23/24/25
S: (1/2-)7-16-36/37-45 |
 |
|

|
Ethanol
is highly flammable. Inhalation may cause cough, headache, fatigue and drowsiness. It causes dry skin and redness
of eyes. Wear protective gloves and goggles.
R: 11 S: (2-)7-16 |
|

|
Propan-1-ol
is irritating and highly flammable. Inhalation may cause ataxia, confusion, dizziness, drowsiness, headache,
nausea and weakness. It can cause dry skin, redness of eyes, pain and blurred
vision. Wear protective gloves and goggles.
R: 11-41-67 S: (2-)7-16-24-26-39
|
 |
|

|
Propan-2-ol
is irritating and highly flammable. Inhalation may cause cough, dizziness, drowsiness, headache and sore
throat. It may cause dry skin and redness of eyes. Wear protective gloves and
goggles.
R: 11-36-67 S:
(2-)7-16-24/25-26
|
 |
The solutions of potassium
dichromate (0.25 mol/L), sulphuric acid (4 mol/L) and solutions of methanol,
ethanol, propan-1-ol and propan-2-ol (2.25 mol/L) are needed for the
experiment. For the experiment all mentioned solutions and deionised water have
to be in equal ten millilitre dropping bottles. In each experiment three drops
of the solution of the oxidising agent, are combined on a blister with three
drops of selected alcohol and three drops of acid. In the blank solution, alcohol
is replaced with deionised water.
Measurements are performed with the
red LED. Transmittance of the blank solution is set to 100.0. Measurements are
started when the acid is added to the mixture of the oxidising agent and an
alcohol. Measurements are recorded every 30 seconds.
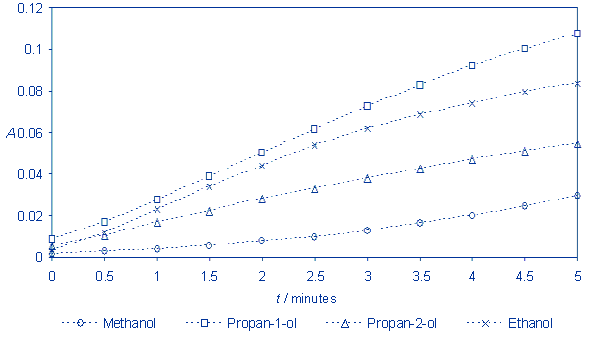
Calculate the absorbance and present
the results on the graph.
Explanation
The reaction runs the fastest with
propan-1-ol and the slowest with methanol. It is possible to observe the
impact of alkyl radical length on the oxidation rate. The longer the
alkyl radical, the faster the oxidation. Could this rule be generalized? What is the effect of radical
branching on the reaction rate?
Developed
and prepared
by: Nataša Gros,
University of Ljubljana, Faculty
of Chemistry and Chemical Technology and
Margareta Vrtačnik, University
of Ljubljana, Faculty of Natural
Sciences and Engineering
|
