|

Effect of dilution on chemical equilibrium
Objective
The objective of this activity is to find out how dilution affects solutions of different substances.
Equipment and reagents
- SpektraTM spectrometer
- KMnO4 solution 10 mmol/L
- FeCl3 solution 10 mmol/L
- Sodium salicylate solution 0.1 mol/L
- KSCN solution 0.1 mol/L
- Deionised water
Hazards
   |
KMnO4 is harmful if swallowed, inhaled or absorbed through the skin. It is a powerful oxidant and reacts vigorously with organic substances. Use goggles and a lab coat, and avoid contact with skin. Do not dispose of the substance into the environment.
Risk phrases: 22, 8, 50/53 Safety phrases: 60, 61 |
 |
Sodium salicylate is harmful if swallowed. Avoid contact with skin and eyes.
Risk phrase: 22 Safety phrases: 24/25 |
 |
KSCN is harmful by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed. Contact with acids liberates very toxic gas. Keep away from food, drink and animal foodstuffs.
Risk phrases: 20/21/22, 32 Safety phrase: 13 |
|

|
FeCl3. 6H2O is harmful if swallowed, irritating to the skin. In the event of contact with the eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice. Risk of serious damage to eyes. Use goggles.
Risk phrases: 22, 38, 41 Safety phrases: 26, 39
|
Procedure
Prepare a blank, solutions of potassium manganate(VII) and solutions of iron(III) complexes with salicylate and tiocyanate in four successive hollows of a blister as specified in the table. Mix thoroughly and measure the transmittance of each solution against the blank using an appropriate LED. Record the measurements and calculate the absorbance.
|
1. 
(Blank)
|
2. 
(KMnO4)
|
3. 
(Fe-salicylate)
|
4. 
(Fe-tiocyanate)
|
Deionised water |
5  |
4  |
3  |
3  |
KMnO4 |
- |
1  |
- |
- |
FeCl3 |
- |
- |
1  |
1  |
Sodium salicylate |
- |
- |
1  |
- |
Potassium tiocyianate |
- |
- |
- |
1  |
Mix thoroughly |
LED for measuring transmittance against blank |
Green |
Blue |
Blue |
T (%) before dilution |
 |
 |
 |
A before dilution |
 |
 |
 |
Add four drops of deionised water to the blank and to each of the solutions, mix thoroughly and repeat the transmittance measurements and absorbance calculations as indicated in the table below.
|
1. 
(Blank)
|
2. 
(KMnO4)
|
3. 
(Fe-salicylate)
|
4. 
(Fe-tiocyanate)
|
Deionised water |
4  |
4  |
4  |
4  |
Mix thoroughly |
LED for measuring transmittance against blank |
Green |
Blue |
Blue |
T (%) after dilution |
 |
 |
 |
A after dilution |
 |
 |
 |
Results
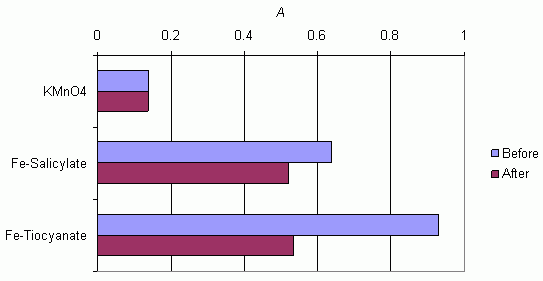
The bar chart demonstrates the differences in absorbances measured before and after dilution of solutions with deionised water. The difference is small for potassium manganate(VII) and explicable by the slightly altered optical geometry due to the enhanced liquid layer. In the other two cases, the absorbance can be observed to decrease significantly after dilution which shows that dilution has affected the chemical equilibrium by causing partial dissociation of the complexes.
Developed and prepared by: Nataša Gros, University of Ljubljana, Faculty of chemistry and chemical technology
|