|

Determination of pKa of bromophenol blue indicator
Objective
The objective of this activity is to determine the pKa of bromophenol blue indicator.
Equipment and reagents
- SpektraTM spectrometer
- Bromophenol blue indicator solution
- HCl solution 2 mol/L
- HCl solution 0.1 mol/L
- NaOH solution 2 mol/L
- Buffer solutions pH 2-10,5
Hazards
 |
NaOH is a corrosive substance, causing burns to eyes, skin, and it is a digestive system irritant. Avoid contact with skin and eyes. Use goggles and a lab coat for personal protection.
Risk phras: 34 Safety phrases: 23, 24/25, 26, 36/37/39, 28 |
 |
Hydrochloric acid is corrosive, irritating to the eyes, the respiratory system and the skin. In the event of contact with the eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice.
Risk phrases: R 36/37/38 Safety phrase: S 26 |
Procedure
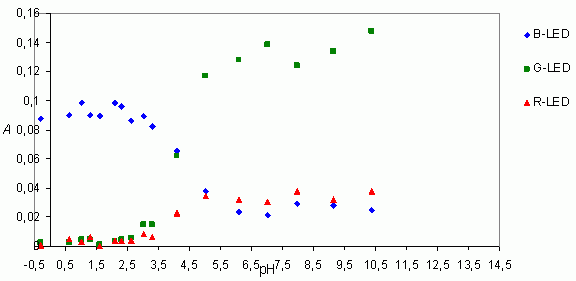
Prepare a blank on a blister by measuring 300 µl of deionised water. To 150 µl of the bromophenol blue solution on a blister add 150 µl of solutions with different pH. Measure the transmittance of each solution against the blank using the blue LED. Record the measurements and calculate the absorbances. Repeat the procedure using a green and then a red LED. Draw a diagram as demonstrated below.
Results
The pH at which the concentrations of protonated and deprotonated molecules are equal corresponds to the pKa. pKa can be determined from the curves obtained by blue (B-LED) or green LED (G-LED) by reading a pH of the point on the curve for which the absorbance is reduced to the half of its range. The result in this case is pKa 4.0.
Developed and prepared by: Nataša Gros, University of Ljubljana, Faculty of chemistry and chemical technology
|