|

HOW MUCH SUGAR IS IN 100 mL OF PREPARED DRINK?
Objective
The objective of this activity is determining by spectrometry how much sugar is in 100 mL of a coloured drink which students prepare from syrup following the teacher’s instructions.
Consumables and equipment
For the activity the following items are needed:
- Intensively coloured syrup with the sugar content specified on a label. We used the mint syrup (Sirop de menthe, Frucci, 70 g sugar/100 mL, Scamark, France) and black currant syrup, (Sirop de cassis, Frucci, 79 g sladkorja/100 mL, Scamark, France).
- Disposable glasses for water.
- Measuring cylinder 50 mL.
- Beaker 100 mL.
- Glass rod.
- Syringe (1 mL) with a pipette tip with a volumetric mark at 0.4 mL for transfer of the examined solutions on a blister.
- Blister.
- SpektraTM spectrometer.
Procedure
Students should understand that the depth of colour of the drink solution is directly proportional to the concentration of the sugar in the drink. When the drink is diluted the colour and the sugar become equally diluted.
Students follow teacher’s instructions and prepare a drink from syrup (sample) and determine by spectrometry how much sugar is contained in 100 mL of prepared drink. They prepare a set of calibration solutions for which the volume of syrup in 100 mL of the solution is known and measure transmittance (T) of the calibration solutions and the sample using the Spektra TM spectrometer. Students draw a graph of the transmittance dependence on the volume of syrup in 100 mL of the solution and for their sample read from a graph how much syrup their drink contains in100 mL. Students calculate the sugar content in 100 mL of prepared drink from the sugar content in 100 mL of syrup specified on the label, and from the spectrometric determination of the volume of syrup in 100 mL of prepared drink. Students weigh the mass of sugar they determined in their drink. The procedure is illustrated below. The activity can be extended with a discussion about sugars and healthy nutrition.
I. PREPARATION OF THE SAMPLE
1) Prepare a drink following the instructions of the manufacturer.

II. PREPARATION OF THE CALIBRATION SOLUTIONS
2) Pour the specified volume (5,10,15, 20 or 25 mL) of syrup in a measuring cylinder.

3) Dilute syrup with tap water to 50 mL.
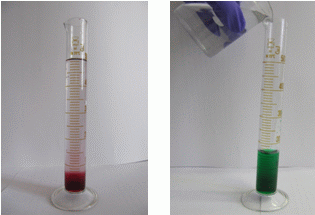
4) Mix well and transfer into a glass.
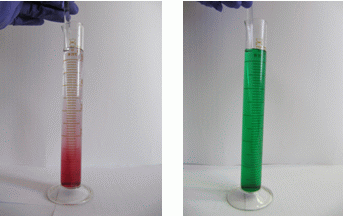
5) Add 50 mL of water to the solution in a glass.
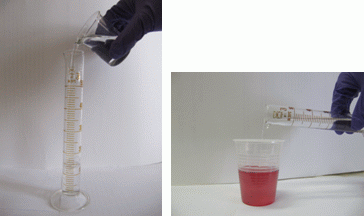
III. SPECTROMETRIC MEASUREMENT

6 ) With an appropriate syringe with a tip transfer 400 µL of tap water into the first hollow of a blister. Proceed with the calibration solutions and the sample.
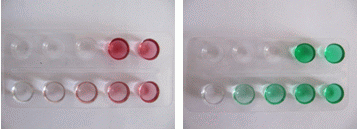
7) Measure the transmittance for the black currant and the mint solutions using the blue LED and the red LED respectively. Set the transmittance reading on 100.0 for water and read transmittance (T) for the calibration solutions and the sample.

IV. RESULTS OF MEASUREMENTS
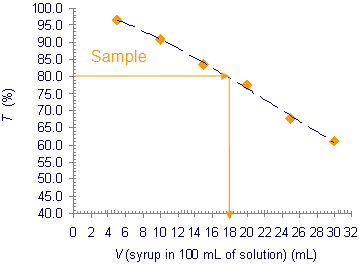
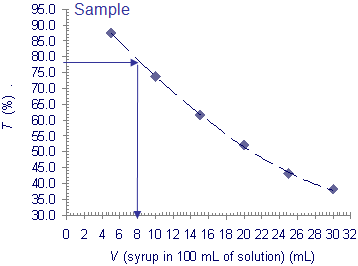
8) Write the transmittance readings in a table and draw a graph as indicated. From the graph read the syrup content in 100 mL of prepared drink?
V (Blackcurrant syrup) (mL) |
Transmittance (%) |
5 |
96.6
|
10 |
90.8 |
15 |
83.5 |
20 |
77.4 |
25 |
67.8 |
30 |
61.0 |
sample |
80.4 |
|
 |
V (Mint syrup) (ml) |
Transmittance (%) |
5 |
87.5 |
10 |
73.6 |
15 |
61.6 |
20 |
52.1 |
25 |
43.0 |
30 |
38.0 |
sample |
78.6 |
|
 |
V. CALCULATING HOW MUCH SUGAR IS IN 100 mL OF PREPARED DRINK
9) Calculate the sugar content in 100 mL of prepared drink from the sugar contained in 100 mL of syrup specified on the label and the spectrometric determination of the volume of syrup in 100 mL of prepared drink.
Blackcurrant syrup |
V (syrup) (mL) |
m (sugar) (g) |
100 |
79 |
18 |
x |
|
Mint syrup |
V (syrup) (mL) |
m (sugar) (g) |
100 |
70 |
8,0 |
x |
|
x=79 g·18 mL/100 mL=14 g |
x=70 g·8 mL/100 mL=5.6 g |
VI. HOW MUCH SUGAR IS THIS?
10) Weigh as much sugar as determined in 100 ml of prepared drink.

Developed and prepared by: Dr. Nataša Gros and Karmen Lampreht, University of Ljubljana, Faculty of Chemistry and Chemical Technology, Slovenia.
|