|

2. The effect of the common ion addition (H+)
on the [Fe3(OH)2(CH3COO)6]+ production The blank solution and the examined solutions are prepared on a blister using a simplified drop-based experimental approach. For the preparation of all the examined solutions, iron(III) and acetate ions are mixed in the ratio 1:4. The solutions differ in a terms of their hydrochloric acid concentration. The transmittance of the examined solutions is measured as in the previous experiment,
absorbance is calculated.
| |
Blank |
Sol. 1 |
Sol. 2 |
Sol. 3 |
Sol. 4 |
Sol. 5 |
|
FeCl3, 0.1 mol/L |
1  |
1  |
1  |
1  |
1  |
1  |
|
CH3COONa, 0.1 mol/L |
- |
4  |
4  |
4  |
4  |
4  |
|
Deionised water |
8  |
4  |
3  |
2  |
1  |
- |
|
HCl, 0.1 mol/L |
- |
- |
1  |
2  |
3  |
4  |
|
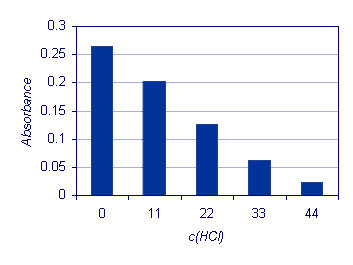
c(HCl) mmol/L |
- |
0 |
11 |
22 |
33 |
44 |
|
Absorbance |
- |
0.264 |
0.202 |
0.126 |
0.063 |
0.023 |
The results, which are presented in a the figure below, demonstrate how a common ion addition (H+) affects the chemical equilibrium. The addition of hydrochloric acid results in the complex decomposition. The chemical equilibrium is shifted towards the reactants: the higher the hydrochloric acid addition, the stronger the influence.
Developed
and prepared
by: Nataša
Gros, University of Ljubljana,
Faculty of Chemistry and Chemical
Technology
|